Table of Contents
The fifth, and final, in a five part series exploring how security teams can identify the most commonly exploited gaps in defenses and leverage their existing security tools to defend against real-world threats.

By Ido Shamriz – Security Researcher
Overview: What is a MITRE ATT&CK Technique?
In the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix for Enterprise, techniques describe the methods an adversary uses to achieve a tactical objective through specific actions. With over 200 techniques and 435 sub-techniques, how should security teams prioritize them?
MITRE ATT&CK Technique Prioritization
To help customers decide what techniques to prioritize, Nagomi analyzed the techniques used most frequently in groups and campaigns. We then cross-referenced the techniques, groups, and campaigns against defenses to pinpoint where security teams can make the most impact. Leveraging our vast dataset encompassing hundreds of campaigns and monitoring millions of assets, the analysis calculates and prioritizes techniques rooted in real-world threats coupled with insights into tool underutilization.
Top MITRE ATT&CK Techniques with the Largest Security Tool Underutilization
Here are the most frequently used techniques with the biggest tool underutilization in cybersecurity today:
What are Remote Services in MITRE ATT&CK Terminology?
In MITRE ATT&CK terminology, Remote Services (T1021) refers to a tactic where adversaries use legitimate remote services to gain unauthorized access to a target system. These services allow attackers to execute actions remotely, bypassing local security controls and enabling lateral movement within a network.
Remote services often include:
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): Enables remote control of Windows systems, and often exploited by attackers for lateral movement and ransomware deployment using stolen credentials or exploiting exposed services.
- Secure Shell (SSH): Provides secure access to Unix systems and is leveraged by attackers for persistence and lateral movement, often using compromised SSH keys to evade detection.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Can be exploited by adversaries to bypass network security and access internal systems, commonly via stolen credentials or misconfigurations.
- Server Message Block (SMB): Facilitates file sharing across networks (Mostly in Windows-Based environment) and is often abused for lateral movement and spreading ransomware via vulnerabilities like EternalBlue.
By leveraging these services, attackers can maintain persistent access and escalate their privileges in the system. In the context of the ATT&CK Matrix, remote services typically fall under the Lateral Movement and Persistence tactics, as they help attackers move between systems and stay hidden within the network.
Example Group Using Remote Services: Leviathan
Leviathan, also known as APT40, is a Chinese state-sponsored cyber espionage group known for targeting entities across multiple sectors, including defense, maritime, aviation, government, and technology. The group is believed to be affiliated with the Chinese Ministry of State Security (MSS) and has been active since at least 2013.
Leviathan has been observed exploiting Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and other remote services to move laterally within victim networks using compromised credentials. This allows them to access and control additional systems while avoiding detection.
To mitigate the risks of remote services like RDP, SSH, VPN, and SMB, organizations should enforce strong Authentication Policies, implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for remote logins, and deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems to monitor and protect sensitive data, significantly reducing the likelihood of adversaries exploiting these services to execute unauthorized code or move laterally across networks.
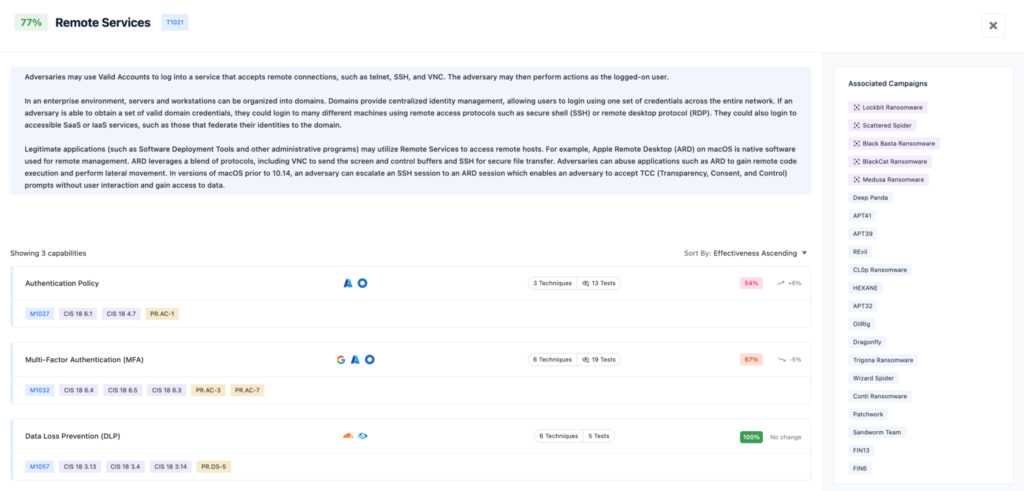
3 Ways to Defend Against Remote Services Technique Using Existing Security Tools
The following section outlines three ways to improve your defense against phishing using the tools you may already have. For each, we’ll start by describing the defensive mechanism and we’ll then use a detailed example.
A. Defending Against Remote Services with Authentication Policy
By implementing a good Authentication Policy, you can dynamically secure and monitor remote access to critical systems by enforcing session time limits, adaptive authentication, and device trust. This approach continuously evaluates session risk based on factors like user behavior and device health, ensuring that remote services such as RDP and VPN are accessed only by authorized users, thus reducing the risk of unauthorized access and session hijacking.
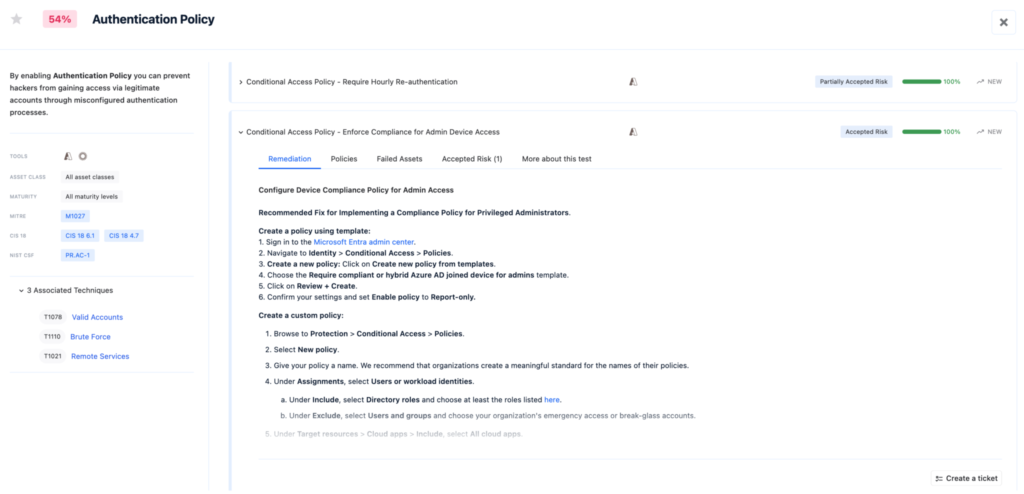
Feature: Enforce Compliance for Admin Device Access
This feature ensures that only devices meeting specific security requirements—such as up-to-date patches, active endpoint protection, and enrollment in a management system—can access administrative tools and resources. If a device fails to comply, access is blocked, preventing potential attackers from using insecure devices to gain control of critical systems, safeguarding privileged accounts and reducing the risk of unauthorized access and exploitation of vulnerabilities.
Example: Using Microsoft Entra
Microsoft Entra enables organizations to create Conditional Access Policies that control access based on user location, device compliance, and risk signals.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center.
- Navigate to Identity > Conditional Access > Policies.
- Create a new policy: Click on Create new policy from templates.
- Choose the Require compliant or hybrid Azure AD joined device for admins template.
- Click on Review + Create.
- Confirm your settings and set Enable policy to Report-only.
B. Defending Against Remote Services with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) policies enforce the use of additional verification methods beyond just a username and password. These policies require users to prove their identity with something they have, such as a phone or hardware token, or something they are, like a fingerprint. By requiring multiple factors, MFA greatly reduces the risk of account compromise from password theft or brute-force attacks, ensuring that even if a password is stolen, unauthorized access is still prevented. Enforcing MFA on critical applications, especially for remote access, protects against credential-based attacks and enhances overall security across the organization.
Feature: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Coverage for all users
This feature ensures that every user within the organization, regardless of their role, must authenticate using multiple factors before accessing resources. This security measure significantly enhances protection by requiring users to prove their identity using two or more methods, such as a password combined with a mobile authenticator or biometric data. By enforcing MFA across the board, organizations minimize the risk of account compromise, even if credentials are stolen or guessed, thus providing a critical defense against phishing, credential stuffing, and brute-force attacks
Example: Using Okta (Classic Engine)
Okta’s comprehensive MFA coverage strengthens security by requiring all users to authenticate through multiple verification methods.
In Okta Classic Engine:
- Access your Okta Admin Console
- Navigate to Security → Authentication
- Click the Sign On tab
- Select the existing Sign On policy that requires modification, or create a new Sign On policy
- Add or edit a rule, ensuring that the Required option under Multifactor Authentication (MFA) is checked
- Save your changes
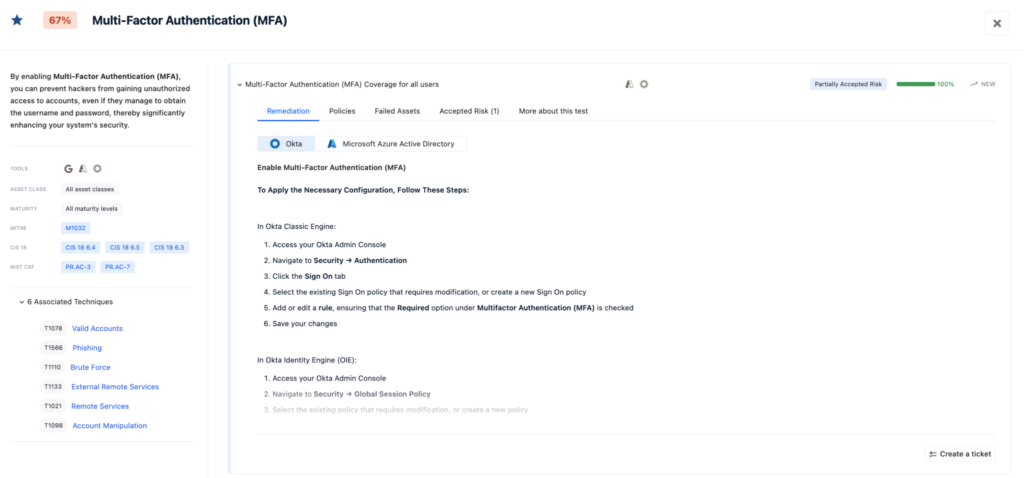
As seen above, Nagomi identifies each security tool that supports MFA configuration. In this case, the security tools are Okta and Microsoft Azure Active Directory. Through compensating controls, Nagomi can determine if MFA is enabled in any of these tools, ensuring that the environment as a whole is fully utilizing available security features. This holistic approach allows organizations to streamline their security management, ensuring comprehensive protection by leveraging the capabilities of their existing infrastructure without redundancy or gaps.
C. Defending Against Remote Services with Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) can help defend against the Remote Services technique by monitoring and controlling the flow of sensitive data over remote access channels. DLP policies can be configured to detect and block unauthorized attempts to transfer confidential information outside of the organization’s network via remote services. By preventing data exfiltration through these channels, DLP reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures that sensitive information remains secure even when accessed remotely by employees or potential attackers.
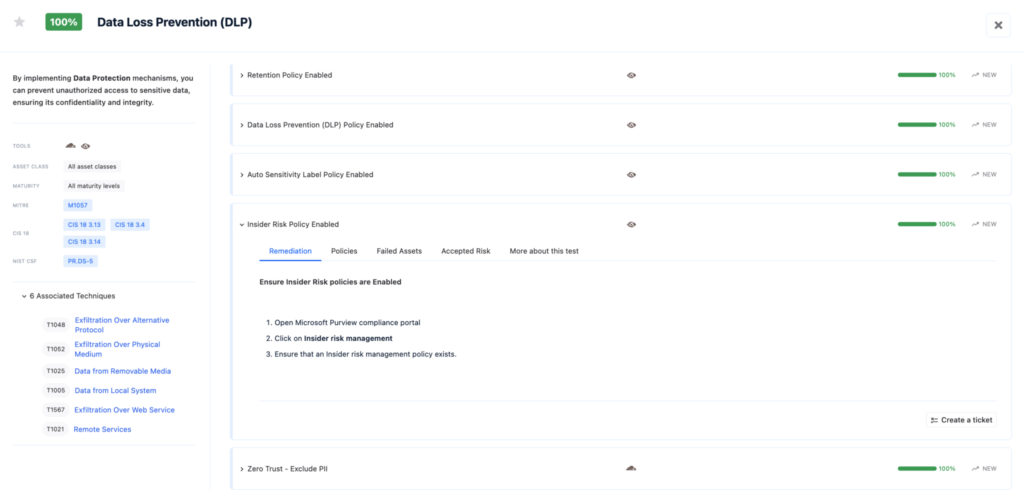
Feature: Insider Risk Policy
This feature helps organizations detect and mitigate insider threats by analyzing user activities for risky behaviors, such as unauthorized data access or leaks. Using machine learning, it identifies potential threats and allows security teams to investigate and act before incidents escalate, ensuring sensitive information is protected from insider misuse.
Example: Using Microsoft Purview
Microsoft Purview is a unified data governance solution that helps organizations protect sensitive information. In order to Ensure Insider Risk policies are Enabled:
- Ensure that an Insider risk management policy exists.
- Open Microsoft Purview compliance portal
- Click on Insider risk management
Summary
This analysis highlights the importance of prioritizing cybersecurity techniques to protect against threats like Remote Services. These services, such as RDP, SSH, VPN, and SMB, are commonly exploited by adversaries to gain unauthorized access and move laterally across networks.
Nagomi’s analysis reveals that Remote Services, among other techniques, suffers from significant tool underutilization, in terms of security tools, making it a critical area for improvement.
By analyzing real-world campaigns and threat data, Nagomi identifies key areas where organizations can leverage existing tools to bolster their defenses.
To mitigate the risks associated with Remote Services – implementing strong Authentication Policies, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems are crucial. For instance, MFA helps reduce unauthorized access by requiring multiple verification factors, while DLP monitors and controls sensitive data transfers over remote channels, preventing data exfiltration.
By adopting these measures and leveraging existing tools more effectively, organizations can bolster their defenses against remote service exploitation and improve their overall security posture.
To see how Nagomi can help you maximize the effectiveness of your tools, check out the Nagomi Proactive Defense Platform or book a demo.



